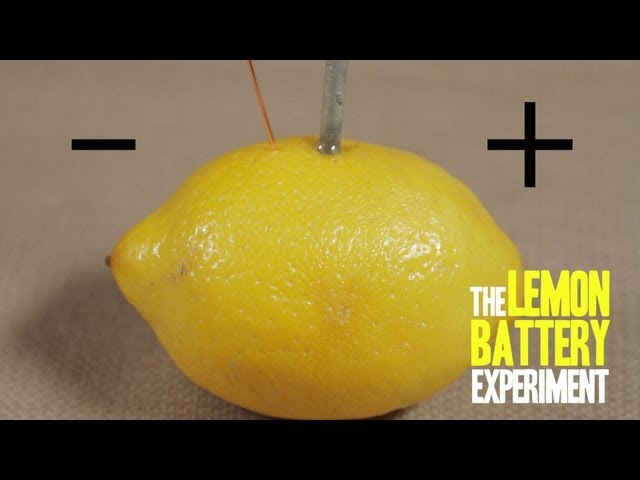
A lemon battery science project is a simple and fun way to learn about how batteries work. By using a lemon, a few nails, and some copper wire, you can create a working battery that can power a small light bulb or other electronic device.
Lemon batteries are a great way to teach kids about science, and they can also be used to power small electronics projects. They are also a good way to learn about renewable energy sources.
Here are the steps on how to make a lemon battery:
- Cut a lemon in half.
- Push a nail into each half of the lemon.
- Connect the two nails with a piece of copper wire.
- Attach the ends of the wire to the terminals of a small light bulb or other electronic device.
The lemon battery will start to produce electricity, which will power the light bulb or other device. The amount of electricity that the battery produces will depend on the size of the lemon and the number of nails that are used.
Lemon batteries are a great way to learn about how batteries work, and they can also be used to power small electronics projects. They are also a good way to learn about renewable energy sources.
Lemon Battery Science Project
A lemon battery science project is a simple and fun way to learn about how batteries work. By using a lemon, a few nails, and some copper wire, you can create a working battery that can power a small light bulb or other electronic device.
- Educational: Lemon batteries are a great way to teach kids about science, and they can also be used to power small electronics projects.
- Renewable energy: Lemon batteries are a good way to learn about renewable energy sources.
- Simple: Lemon batteries are easy to make and require only a few materials.
- Inexpensive: Lemon batteries are inexpensive to make, making them a great option for schools and other educational settings.
- Safe: Lemon batteries are safe to make and use, making them a good choice for children.
- Fun: Lemon batteries are a fun and engaging way to learn about science.
Lemon batteries are a great way to learn about how batteries work, and they can also be used to power small electronics projects. They are also a good way to learn about renewable energy sources. In addition, lemon batteries are simple, inexpensive, safe, and fun to make, making them a great option for schools and other educational settings.
Educational
Lemon battery science projects are a great way to teach kids about science because they are simple, inexpensive, and fun. They also provide a hands-on way to learn about how batteries work and how to generate electricity from renewable sources. In addition, lemon battery science projects can be used to power small electronics projects, such as LED lights, small motors, and even calculators.
The educational value of lemon battery science projects is significant. By building a lemon battery, students can learn about the following scientific concepts:
- The basic principles of electrochemistry
- The role of acids in generating electricity
- The concept of a closed circuit
- How to measure voltage and current
Lemon battery science projects can also be used to teach students about renewable energy sources. By using a lemon to generate electricity, students can learn about the potential of renewable energy sources to power our homes and businesses.
In addition to their educational value, lemon battery science projects are also a lot of fun. Students enjoy building and experimenting with lemon batteries, and they are often amazed by how much power they can generate from a simple lemon.
Lemon battery science projects are a great way to teach kids about science, renewable energy, and electricity. They are simple, inexpensive, and fun, and they can be used to power small electronics projects. If you are looking for a fun and educational science project to do with your kids, I highly recommend building a lemon battery.
Renewable energy
Lemon battery science projects are a great way to learn about renewable energy sources because they provide a hands-on way to generate electricity from a renewable source. By using a lemon, a few nails, and some copper wire, students can create a working battery that can power a small light bulb or other electronic device.
-
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy is energy that comes from natural resources that can be replenished, such as sunlight, wind, and water. Lemon batteries are a good way to learn about renewable energy because they use a lemon to generate electricity, which is a renewable resource. -
How do lemon batteries work?
Lemon batteries work by using the chemical energy stored in the lemon to generate electricity. When the nails and copper wire are inserted into the lemon, the acid in the lemon reacts with the metal to create an electrical current. This current can then be used to power a small light bulb or other electronic device. -
What are the benefits of using renewable energy?
There are many benefits to using renewable energy, including reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and creating jobs. Lemon batteries are a good way to learn about the benefits of renewable energy because they provide a simple and inexpensive way to generate electricity from a renewable source. -
How can I use lemon batteries to learn about renewable energy?
There are many ways to use lemon batteries to learn about renewable energy. One way is to build a lemon battery and use it to power a small light bulb or other electronic device. Another way is to use a lemon battery to charge a battery-powered toy or gadget. You can also use lemon batteries to power small science projects, such as a homemade electric motor or a water pump.
Lemon battery science projects are a great way to learn about renewable energy sources. They are simple, inexpensive, and fun, and they can be used to power small electronics projects. By using lemon batteries to generate electricity, students can learn about the potential of renewable energy sources to power our homes and businesses.
Simple
The simplicity of lemon batteries is one of their key advantages, making them an ideal choice for educational purposes and quick science experiments.
- Easy to assemble: Lemon batteries require only a few basic materials, such as a lemon, nails, copper wire, and a light bulb or other small electronic device. This makes them easy to assemble, even for young children.
- No special tools required: Lemon batteries can be assembled without the need for any special tools. This makes them a great option for simple science projects and demonstrations.
- Inexpensive: The materials required to make a lemon battery are inexpensive and readily available, making them a cost-effective option for educational and experimental purposes.
- Quick to set up: Lemon batteries can be assembled quickly and easily, making them a great option for quick science experiments or demonstrations.
The simplicity of lemon batteries makes them a great choice for educational purposes and quick science experiments. They are easy to assemble, require no special tools, are inexpensive, and can be set up quickly.
Inexpensive
The low cost of lemon batteries makes them an excellent choice for schools and other educational settings. Here are a few reasons why:
- Materials are readily available and affordable: Lemons, nails, and copper wire are all inexpensive and easy to find, making it easy for schools to acquire the necessary materials for lemon battery science projects.
- No specialized equipment required: Lemon batteries can be assembled using simple tools that are commonly found in schools, such as scissors, pliers, and wire strippers. This eliminates the need for expensive or specialized equipment.
- Scalability: Lemon batteries can be easily scaled up or down depending on the needs of the project. For example, a small lemon battery can be used to power a single LED light, while a larger lemon battery can be used to power a small motor or other device.
- Reusable: Lemon batteries can be reused multiple times, which further reduces the cost per experiment. Simply replace the lemon when it is no longer producing enough electricity.
The inexpensiveness of lemon batteries makes them an ideal choice for schools and other educational settings. They are easy to assemble, require no specialized equipment, and can be reused multiple times. This makes them a cost-effective way to teach students about science, electricity, and renewable energy.
Safe
The safety of lemon batteries is a key factor in their suitability for use in educational settings, particularly with children. Unlike many other types of batteries, lemon batteries do not contain any hazardous materials or produce any harmful fumes. This makes them a much safer option for children to handle and experiment with.
The lack of hazardous materials and harmful fumes associated with lemon batteries is due to their simple construction and the use of natural materials. Lemons are a common fruit that is readily available and inexpensive. Nails and copper wire are also commonly found in homes and hardware stores. These materials are all non-toxic and safe to handle.
The safety of lemon batteries is further enhanced by their low voltage output. Lemon batteries typically produce only about 1-2 volts of electricity, which is not enough to cause any harm to humans or animals. This low voltage also makes lemon batteries safe to use in conjunction with other electronic components, such as LEDs and small motors.
The safety of lemon batteries makes them an ideal choice for use in lemon battery science projects. Children can safely assemble and use lemon batteries to learn about science, electricity, and renewable energy without the need for adult supervision.
Fun
The “fun” aspect of lemon battery science projects plays a vital role in fostering engagement and promoting effective learning. Here’s how this fun element manifests in these projects and its implications:
- Hands-on Experience: Lemon battery science projects provide a hands-on approach to learning, allowing students to actively participate in the process of generating electricity from a lemon. This interactive experience makes the learning process more enjoyable and memorable.
- Visual Appeal: The use of a lemon as the main component adds a visual appeal to the project. The bright yellow color of the lemon, along with the bubbling reaction that occurs when the nails and copper wire are inserted, captures students’ attention and makes the learning experience more engaging.
- Sense of Accomplishment: When students successfully create a working lemon battery and observe it powering a small device, they experience a sense of accomplishment. This positive reinforcement further motivates them to explore scientific concepts and encourages them to pursue further learning.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Lemon battery science projects can be conducted in groups, fostering collaboration and teamwork among students. Working together to assemble the battery and troubleshoot any issues promotes communication, problem-solving skills, and a shared sense of achievement.
In summary, the “fun” element of lemon battery science projects lies in their hands-on nature, visual appeal, sense of accomplishment, and potential for collaboration. These factors contribute to a positive and engaging learning experience, making these projects an effective tool for teaching science concepts and fostering a passion for STEM subjects.
FAQs on Lemon Battery Science Projects
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to lemon battery science projects, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns or misconceptions:
Question 1: How much electricity can a lemon battery produce?
A lemon battery typically produces a voltage of around 0.5 to 1 volt, which is relatively low compared to other types of batteries. However, the amount of current it can provide depends on the size of the lemon and the number of nails and copper wires used.
Question 2: Can lemon batteries be used to power practical devices?
While lemon batteries produce a small amount of electricity, they can be used to power small, low-power devices such as LEDs, calculators, and small motors. However, they are not suitable for powering high-power devices like smartphones or laptops.
Question 3: Are lemon batteries safe?
Yes, lemon batteries are generally safe to make and use. They do not contain any hazardous materials or produce harmful fumes. However, it’s important to supervise children when they are working with lemon batteries to ensure proper handling and avoid any potential risks.
Question 4: How long do lemon batteries last?
The lifespan of a lemon battery depends on factors such as the size of the lemon, the number of nails and copper wires used, and the amount of current it is providing. Typically, a lemon battery can last for several hours to a few days, but its performance will gradually decrease over time.
Question 5: Can lemon batteries be recharged?
No, lemon batteries cannot be recharged once they are discharged. The chemical reaction that produces electricity in a lemon battery is irreversible, so once the lemon’s juice is depleted, the battery will no longer produce electricity.
Question 6: What are the educational benefits of lemon battery science projects?
Lemon battery science projects are valuable educational tools that can teach students about basic electricity, chemical reactions, and renewable energy sources. They provide a hands-on and engaging way to explore scientific concepts and foster an interest in STEM subjects.
In summary, lemon battery science projects offer a safe, simple, and educational way to learn about electricity and renewable energy. They are suitable for students of all ages and can be easily adapted to various learning environments.
Transition to the next article section:
For further information on lemon battery science projects, including detailed instructions, safety guidelines, and troubleshooting tips, please refer to the additional resources provided in the next section.
Tips on Lemon Battery Science Projects
Lemon battery science projects are a great way to teach kids about science, and they can also be used to power small electronics projects. Here are a few tips to help you get started:
Tip 1: Use fresh lemons. Fresh lemons will produce more electricity than old or bruised lemons. You can tell if a lemon is fresh by its weight. A fresh lemon will be heavy for its size.
Tip 2: Use clean nails and copper wire. Clean nails and copper wire will conduct electricity better than dirty or rusty ones. You can clean your nails and copper wire with a brillo pad or sandpaper.
Tip 3: Insert the nails and copper wire deeply into the lemon. The deeper you insert the nails and copper wire, the more surface area will be in contact with the lemon juice, and the more electricity the battery will produce.
Tip 4: Connect the nails and copper wire to the terminals of a small light bulb or other electronic device. You can use alligator clips or electrical tape to connect the nails and copper wire to the terminals of the light bulb or other electronic device.
Tip 5: Experiment with different sizes and shapes of lemons. You can use different sizes and shapes of lemons to create batteries with different voltages and currents. For example, a large lemon will produce more electricity than a small lemon, and a lemon that is cut in half will produce more electricity than a whole lemon.
Summary:
- Fresh lemons produce more electricity.
- Clean nails and copper wire conduct electricity better.
- Inserting the nails and copper wire deeply into the lemon increases the surface area and electricity production.
- Connecting the nails and copper wire to a light bulb or other electronic device powers it.
- Experimenting with different sizes and shapes of lemons varies the battery’s voltage and current.
By following these tips, you can create a lemon battery that will power a small light bulb or other electronic device. Lemon battery science projects are a great way to teach kids about science, and they can also be used to power small electronics projects.
Conclusion
Lemon battery science projects provide a simple, inexpensive, and engaging way to introduce students to the fundamental principles of electrochemistry and renewable energy. Through hands-on exploration, learners gain a practical understanding of how batteries generate electricity and how they can harness the power of nature to do so.
By combining the accessibility of lemons with the principles of science, lemon battery projects foster a spirit of inquiry and experimentation. They empower students to ask questions, make predictions, and test their hypotheses, nurturing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Moreover, the projects highlight the importance of sustainability and encourage students to consider the potential of renewable energy sources in addressing global challenges.
Youtube Video: